Laboratory Equipment, Mass Spectrometry
Mass Spectrometry Troubleshooting and Common Issues
Introduction
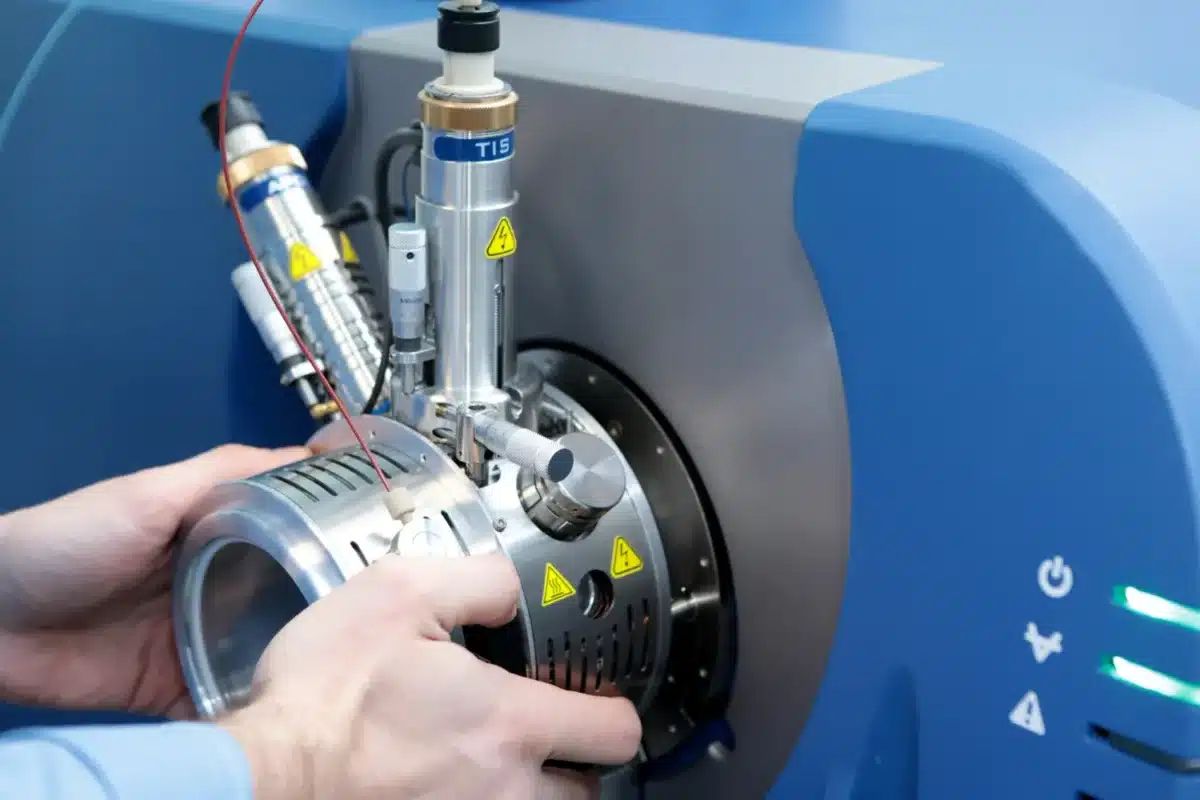
Mass spectrometry (MS) is a powerful analytical technique in various scientific fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science. It allows researchers to identify and quantify compounds with high precision and sensitivity. However, like any analytical method, mass spectrometry has challenges. In this blog post, we will explore some common issues that can arise during mass spectrometry experiments and provide troubleshooting tips to help you overcome them.
gmi service departmentPoor Signal Intensity
One of the most common issues encountered in mass spectrometry is poor signal intensity. This can result in weak or undetectable peaks in your mass spectra, making it difficult to identify or quantify your target compounds. Several factors can contribute to poor signal intensity:
a. Sample Concentration: Ensure that your sample is appropriately concentrated. You may not get a strong enough signal if it’s too dilute. Conversely, if it’s too concentrated, it could cause ion suppression.
b. Ionization Efficiency: The choice of ionization technique can significantly affect signal intensity. Experiment with different ionization methods (e.g., ESI, MALDI, APCI) to optimize ionization efficiency for your analytes.
c. Tune and Calibrate: Regularly tune and calibrate your mass spectrometer to ensure it operates at peak performance. This includes checking the ion source, mass analyzer, and detector settings.
Mass Accuracy and Resolution Problems
Accurate mass determination and high-resolution mass spectrometry are essential for precise compound identification. If you’re experiencing issues with mass accuracy or resolution, consider the following:
a. Mass Calibration: Perform regular mass calibration using appropriate standards to ensure accurate mass measurements. Incorrect calibration can lead to mass errors.
b. Mass Spectrometer Maintenance: Keep your mass spectrometer in good working condition by following the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines. Contaminants or instrument drift can affect mass accuracy and resolution.
Peak Splitting and Broadening
Peak splitting and broadening in mass spectra can make identifying compounds and distinguishing isomers challenging. Common causes include:
a. Column and Sample Contaminants: Contaminants in the sample or on the chromatographic column can lead to peak splitting or broadening. Ensure proper sample preparation and column maintenance.
b. Ionization Conditions: Adjusting ionization conditions (e.g., source parameters, gas flows) can help reduce peak broadening.
Ion Suppression and Matrix Effects
Ion suppression occurs when co-eluting compounds in your sample interfere with the ionization of your target analytes. This often happens in complex matrices or samples containing high salt concentrations or detergents. To address ion suppression:
a. Sample Cleanup: To remove interfering substances, use sample cleanup techniques such as solid-phase extraction (SPE) or liquid-liquid extraction (LLE).
b. Matrix-Matched Standards: Prepare matrix-matched standards to compensate for matrix effects and improve quantification accuracy.
Baseline Drift and Noise
Baseline drift and noise can obscure your mass spectra and make it challenging to detect low-abundance compounds. To reduce baseline drift and noise:
a. Optimize Chromatography: Fine-tune your chromatographic conditions to obtain a stable baseline.
b. Detector Settings: To minimize noise, adjust detector settings (e.g., gain, filter settings).
schedule a free consultation with a GMI technical sales expertConclusion
Mass spectrometry is a versatile analytical technique but can be prone to various common data quality issues. By understanding these issues and implementing troubleshooting strategies, you can improve the reliability and accuracy of your mass spectrometry experiments. Regular instrument maintenance, careful sample preparation, and method optimization are essential for successful mass spectrometry analysis.